Insulin resistance is a growing health condition that affects millions of people, yet it often goes undiagnosed until more serious issues arise. Despite its prevalence, many are unaware of what insulin resistance truly is, how it develops, or the long-term consequences it can have on overall health. In this blog post, we’ll dive into what insulin resistance is, how it affects the body, and how Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs) can be used to help people manage their health.

What Is Insulin Resistance?
Insulin is a hormone secreted by the pancreas in response to elevated blood sugar levels when we eat. Its function is to remove glucose from the blood and send it to the cells to use as energy or for storage. Insulin resistance occurs when the body’s cells—primarily in muscle, fat, and the liver—become less sensitive to insulin and no longer respond to it. This causes blood sugar to remain high (since it is not being converted to energy as easily) and your body will produce more insulin to try and compensate for this. Over time, this can lead to high levels of insulin in the blood, which can contribute to weight gain, fat accumulation, and other metabolic issues. If left uncontrolled, insulin resistance can eventually progress to Type 2 diabetes.
The early signs of insulin resistance are often subtle and may not be obvious. Some of the common symptoms and risk factors include:
- Fatigue
- Difficulty losing weight
- High blood pressure
- High triglycerides
- Abdominal obesity (fat around the belly)

What causes Insulin Resistance?
Lifestyle factors and genetics can influence the risk of Insulin Resistance including:
- Obesity
- History of gestational diabetes
- Family history of diabetes
- High Blood Pressure
- High Cholesterol
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)
- Metabolic Syndrome
- Living a sedentary lifestyle
- Overnutrition
- Excessive alcohol intake

How Insulin Resistance Affects the Body
When insulin resistance develops, glucose builds up in the bloodstream because it can’t be efficiently moved into cells. This leads to a variety of potential health issues:
- Chronic inflammation: Insulin resistance is often associated with chronic inflammation, which is a known contributor to cardiovascular disease, cancer, and other chronic conditions.
- Fatty liver disease: The liver becomes overwhelmed with excess glucose and insulin, which may lead to the accumulation of fat in the liver (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease).
- Higher risk of heart disease: Insulin resistance increases the risk of developing high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and atherosclerosis, all of which contribute to cardiovascular disease.
As you can see, insulin resistance is a serious condition that can have wide-reaching effects on health. The good news is that there is a lot we can do to identify glucose dysregulation early on, like assessing various lab metrics, utilizing continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), and leveraging personalized nutrition interventions.
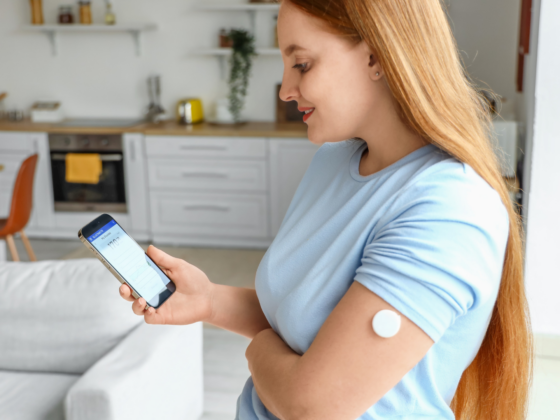
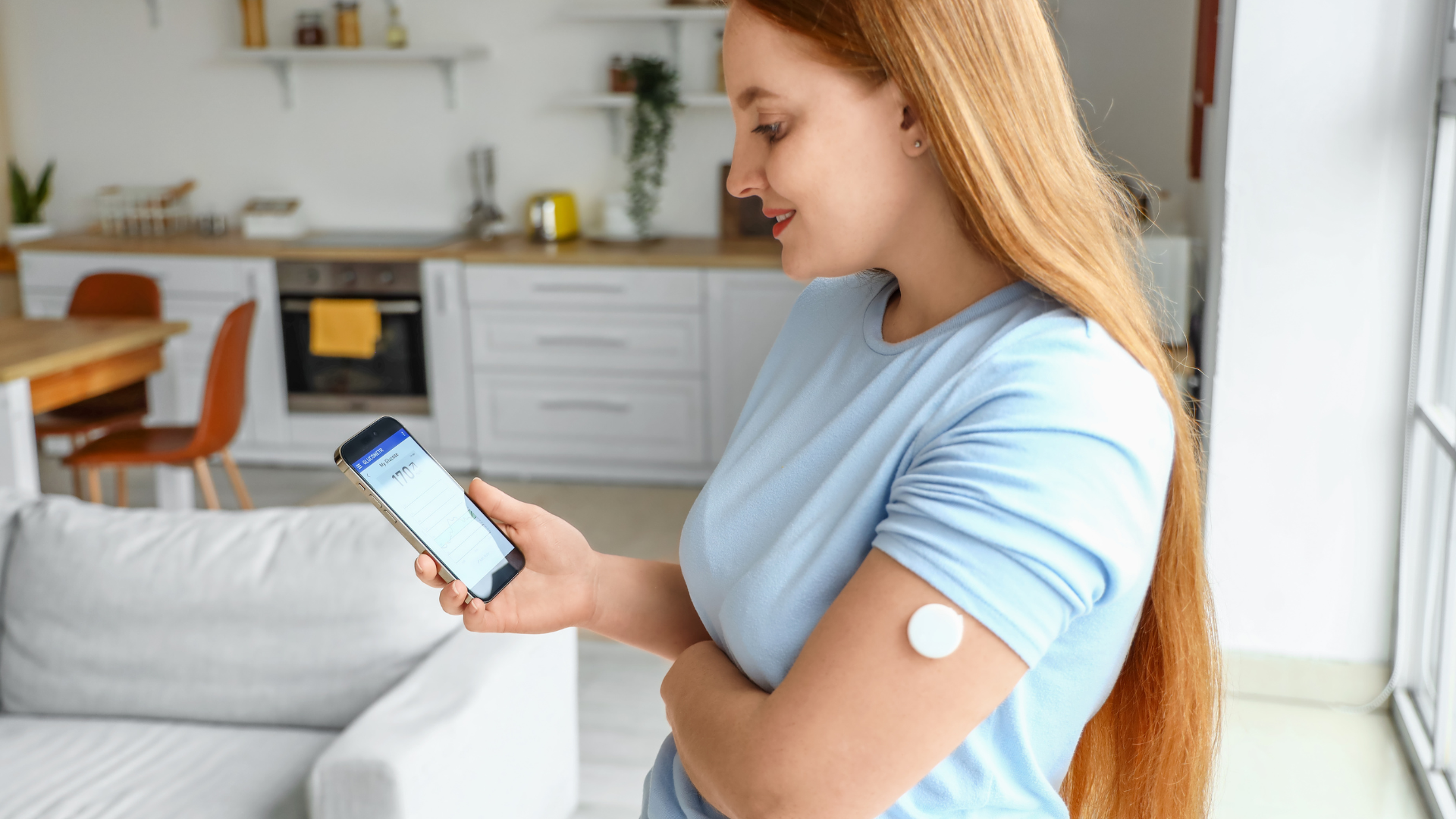
What Is a CGM?
A CGM is a small, wearable device that provides real-time data on your blood glucose levels throughout the day. Unlike traditional blood glucose meters, which require a finger prick to test blood at specific intervals, a CGM continuously measures glucose in the interstitial fluid via a small sensor inserted under the skin, typically worn on the arm. The sensor is connected to a transmitter that sends the data to an app on your phone or other device, providing users with continuous feedback on their blood sugar levels.
The primary advantage of CGMs is that they offer real-time insights into how diet, exercise, stress, and sleep affect glucose levels. This can be really helpful when making decisions about dietary and lifestyle choices to optimize metabolic health.
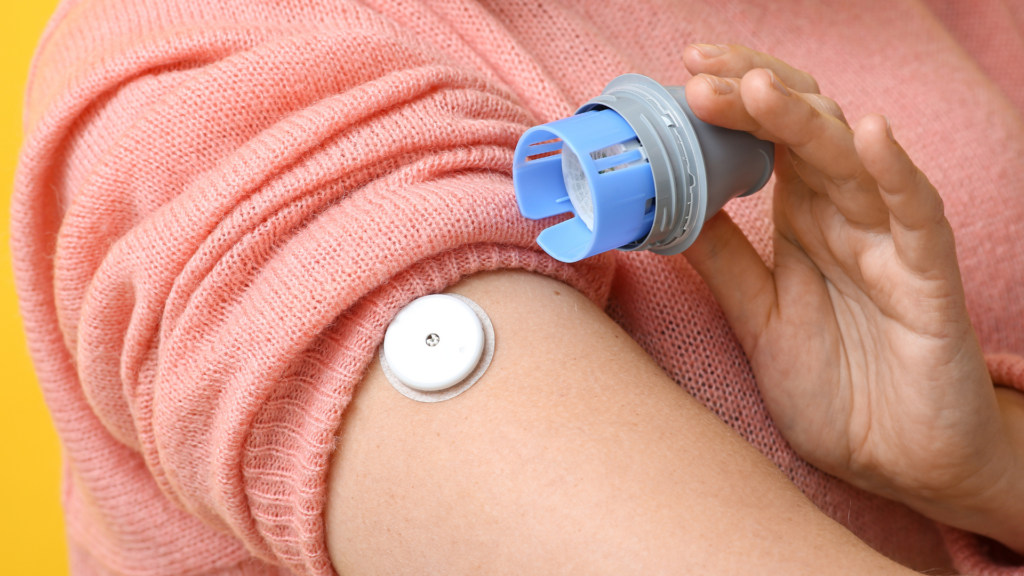
How CGMs Help with Insulin Resistance
For people with insulin resistance or those at risk of developing it, CGMs can be a game-changer. Here’s how they can help:
- Tracking Blood Sugar Trends: A CGM provides continuous, real-time data on your blood sugar levels, allowing you to see trends over time. This is especially useful because insulin resistance can cause blood sugar to fluctuate, and subtle changes may be missed with periodic testing. By tracking these fluctuations, individuals can adjust their diet and lifestyle to stabilize their blood sugar.
- Personalized Insights for Dietary Choices: Certain foods, such as refined carbohydrates and sugary snacks, can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar. A CGM allows users to see the immediate impact of what they’re eating on their glucose levels, helping them identify which foods are problematic and which ones help maintain stable blood sugar.
- Exercise and Stress Monitoring: Physical activity and stress levels both affect blood sugar. With a CGM, you can observe how different types of exercise or moments of high stress influence your glucose levels. This can guide you to modify your workout routine or stress management techniques for better control of your blood sugar.
- Early Warning of Blood Sugar Spikes: Since insulin resistance can cause subtle changes in glucose regulation before full-blown diabetes sets in, CGMs provide an early warning system. By detecting hyperglycemic (high blood sugar) or hypoglycemic (low blood sugar) events early, a CGM can help individuals take action to prevent major issues, such as insulin overload or a crash in blood sugar.
- Improved Monitoring of Progress: For those working to reverse insulin resistance, a CGM can be an invaluable tool to track progress. As individuals make lifestyle changes—such as eating a lower-glycemic diet or increasing physical activity—they can see how their glucose levels respond, helping them gauge the effectiveness of their efforts.
Who Should Use a CGM?
CGM’s are increasingly being used by individuals looking to optimize their metabolic health, by using them as a prevention tool and a way to better understand the impact of their diet and lifestyle on their health. Using a CGM can be an excellent way to monitor your glucose levels and make proactive changes to your lifestyle.
CGMs can be especially beneficial for:
- People with insulin resistance or prediabetes: Catching early signs of blood sugar imbalance can prevent further progression to Type 2 diabetes.
- Those with metabolic syndrome: A group of conditions including high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, excess abdominal fat, and abnormal cholesterol levels that increase the risk of heart disease and diabetes.
- Fitness enthusiasts and athletes: Individuals looking to optimize their nutrition and exercise regimens by understanding how their body responds to various foods and workouts.
Right now, CGM’s are only accessible with a prescription. However, there are several companies, like Levels, that make it easier for people to access these devices.
References:
American Diabetes Association. (n.d.). Insulin resistance. Retrieved from https://diabetes.org/health-wellness/insulin-resistance
Cleveland Clinic. (n.d.). Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). Retrieved from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/continuous-glucose-monitoring-cgm
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (n.d.). Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/about/insulin-resistance-type-2-diabetes.html




